Руководство по хирургии: различия между версиями
1 часть перевода хирургии |
мНет описания правки |
||
| Строка 5: | Строка 5: | ||
!Функции | !Функции | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:1Scalpel.png]]<br>'''{{anchor|Scalpel}}[[#Scalpel|Scalpel]]'''||Используется для разрезания плоти. Имеет три варианта лазерного усиления разного качества, каждый из которых имеет процентный шанс не создать кровотечение | |[[File:1Scalpel.png]]<br>'''{{anchor|Scalpel}}[[#Scalpel|Scalpel]]'''||Используется для разрезания плоти. Имеет три варианта лазерного усиления разного качества, каждый из которых имеет процентный шанс не создать кровотечение.<br>'''Импровизированные аналоги:''' PICT system[[File:The_PICT System.png|32px]], штык-нож[[File:Autowiki-M5 'Night Raider' bayonet.png|32px]], кухонный нож[[File:Kitchen_Knife.png|32px]], или осколок стекла[[File:Shard.png|32px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:1Incision_manager.png|64px]]<br>'''{{anchor|Система проведения разрезов}}[[#Incision Management System|Incision Management System]] (IMS)'''||Используется для рассечения плоти, не требует зажима кровотечения и перестановки органов. В основном выполняет функции скальпеля, гемостата и ретрактора в один этап при первичном разрезе. Функционирует как скальпель только на этапах после первого. (Доступен в хирургическом отделении на солнечном гребне) | |[[File:1Incision_manager.png|64px]]<br>'''{{anchor|Система проведения разрезов}}[[#Incision Management System|Incision Management System]] (IMS)'''||Используется для рассечения плоти, не требует зажима кровотечения и перестановки органов. В основном выполняет функции скальпеля, гемостата и ретрактора в один этап при первичном разрезе. Функционирует как скальпель только на этапах после первого. (Доступен в хирургическом отделении на солнечном гребне) | ||
Версия от 16:54, 13 марта 2025
Инструменты для торговли
| Инструмент | Функции |
|---|---|
 Scalpel |
Используется для разрезания плоти. Имеет три варианта лазерного усиления разного качества, каждый из которых имеет процентный шанс не создать кровотечение. Импровизированные аналоги: PICT systemФайл:The PICT System.png, штык-нож |
| Файл:1Incision manager.png Incision Management System (IMS) |
Используется для рассечения плоти, не требует зажима кровотечения и перестановки органов. В основном выполняет функции скальпеля, гемостата и ретрактора в один этап при первичном разрезе. Функционирует как скальпель только на этапах после первого. (Доступен в хирургическом отделении на солнечном гребне) |
| Файл:1Hemostat.png Hemostat |
Используется для остановки кровотечения во время операции или для удаления инородных и нежелательных объектов из тела пациента. Также используется для восстановления мозга путём удаления осколков кости из серого вещества. Импровизированные аналоги: кусачки |
| Файл:1Bone Setter.png Bone Setter |
Используется для вправления костей на место. Если использовать на кости, которая не сломана, то вы сломаете её it. Импровизированные аналоги: ключ |
| Файл:1Bone-Gel.png Bone Gel |
Используется для восстановления сломанных/раздробленных костей, как в случае перелома, так и для реставрации разрушенных грудных клеток и черепов. Импровизированные аналоги: отвёртка |
| Файл:1Retractor.png Retractor |
Используется для расширения разрезов и перестановки органов, а также для перемещения разрезанных грудных клеток и черепов. Большинство скальпелей и его аналогов могут расширять разрезы вместо ретрактора или его заменителей, хотя и гораздо медленнее. При вскрытии костей существует небольшая вероятность перелома грудной клетки или черепа, даже если этот шаг выполнен правильно. Импровизированные аналоги: лом |
| Файл:1Cautery.png Cautery |
Используется для зашивания разрезов на коже пациента. Обжигает кожу. Импровизированные аналоги: сигарета |
| Файл:Fixovein.png Fix-O-Vein |
Используется для восстановления вен и артерий, при этом лечит внутренние кровотечения. Также используется для устранения гематом в головном мозге, лечит тяжёлые повреждения мозга. Импровизированные аналоги: хирургический набор |
| Файл:1Saw.png Circular Saw |
Используется для вырезания костей, особенно в грудной клетке и черепе. Выполнение шага по разрезанию костей при намерении обезоружить мгновенно завершит шаг ценой гарантированного перелома в этой области. Импровизированные аналоги: штык-нож |
 Advanced Trauma Kit |
Используется для восстановления всех органов, кроме мозга и глаз. Импровизированные аналоги: бинты |
 Хирургическая нить |
Используется для сшивания повреждённой плоти, лечения чрезмерной грубой силы. Его также можно использовать для зашивания разрезов вместо прижигателя. Импровизированные аналоги: Fix-O-VeinФайл:Fixovein.png моток кабеля |
| Файл:Synth Graft.png Synth-Graft |
Используется для пересадки сильно обожжённой плоти, лечения чрезмерных ожогов. Отсутствуют импровизированные эквиваленты. |
| Файл:The PICT System.png PICT System |
Прецизионный инструмент для разрезов и прижигания использует высокочастотное вибрирующее лезвие, лазерный прижигатель в сочетании с системой контроля всасывания жидкости для точного рассечения тканей и предотвращения утечки жидкости. Несмотря на непростую программу разработки и пугающую цену, за пределами сложных экспериментальных операций он ничем не лучше обычного двадцатидолларового скальпеля и не может бескровно сделать разрез во всю длину.
Импровизированные аналоги: скальпель |
 Surgical Drill |
Используется для создания отверстий в грудной стенке с целью получения доступа к полостям для имплантатов, будь то имплантация нового объекта с нуля или удаление глубоко внедрившегося инородного тела (например, обезьяньего куба...)
Импровизированные аналоги: ручка или металлический прут |
- Импровизированные инструменты выполняют операции медленнее своих стандартных вариантов и несут риск неудачи, снижаемый вашим хирургическим навыком. Суровость штрафа за скорость зависит от того, насколько непригоден инструмент. Например, штык гораздо лучше заменяет скальпель, чем осколок стекла.
- Помимо штрафа за скорость, импровизированный PICT разбрызгивает кислотную кровь на вас и вашего пациента, нанося ожоги телу пациента, а также повреждая органы - сердце, лёгкие и печень.
Preparing for Surgery
Tools
Before you begin to operate, you should make sure you have all the tools you will need. Occasionally a surgeon will accidentally pocket a tool, or a deploying field surgeon will grab tools out of an operating theatre.
Specifically designed surgical tools are the best, but there are a variety of substitutes; some tools can be used outside of their intended role, and others can be replaced with improvised substitutes.
- The equipment on the Almayer is adequate, but sometimes marines will find better tools while deployed. If someone asks if you'd like an Incision Management System, the correct answer is "yes please".
Surgical Surface
The second requirement is a place to work. Some surgeries can be performed on a standing patient, and it doesn't matter where you perform them. Most, however, need a decent surface to work on.
The patient doesn't necessarily need to be buckled - having them on the same tile will do. However the speed modifier is not applied if they aren't buckled (this excludes the operating table and surfaces with no buckles). If a surface isn't ideal, the surgery will take longer - and possibly a lot longer.
Locations, namely medical tents, can also provide some benefits to the surgery speed and pain reduction required.
- The ideal surface for surgery is a proper operating table.
 This is designed for surgery and has a built-in anesthetic system for patients buckled to it. This is the only surface that can be used for extracting xenomorph larvae.
This is designed for surgery and has a built-in anesthetic system for patients buckled to it. This is the only surface that can be used for extracting xenomorph larvae.
- The next best thing is a portable surgical bed. Файл:FieldSurgicalBed.png
- The worst surfaces are floors and Med-Evac stretchers, Файл:Med Evac Stretcher.png which are not designed for surgery, and trying to work with their fittings in their way is as hard as no surface at all.
Surgery Failure Penalties
Improvised tools and poor working conditions contribute to a penalty system that increases the risk of failure, but this penalty is mitigated by your surgical skill.
| Chance of Surgical Failure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
For example, performing internal bleeding surgery, skipping clamp bleeders step, by a corpsman on a roller:
| Step | Tool Penalties | Surface Penalties | Skill Mitigation | Total Penalties | Chance of Failure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Knife - Incision (Pre-op) | 0 (Subsitute) | - (Lying not required) | 0 (Novice) | 0 | 0% |
| Knife - Expose (Pre-op) | 2 (Awful) | - (Lying not required) | 0 (Novice) | 2 | 25% |
| Surgical Line - Fix Vein (IB) | 0 (Subsitute) | 1 (Unsuited) | 0 (Novice) | 1 | 5% |
| Surgical Line - Suture (Post-op) | 0 (Ideal) | - (Lying not required) | 0 (Novice) | 0 | 0% |
For example, performing internal bleeding surgery, skipping clamp bleeders step, by a surgeon on a roller:
| Step | Tool Penalties | Surface Penalties | Skill Mitigation | Total Penalties | Chance of Failure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shard - Incision (Pre-op) | 2 (Awful) | - (Lying not required) | -1 (Trained) | 1 | 5% |
| Shard - Expose (Pre-op) | 2 (Awful) | - (Lying not required) | -1 (Trained) | 1 | 5% |
| Surgical Line - Fix Vein (IB) | 0 (Subsitute) | 1 (Unsuited) | -1 (Trained) | 0 | 0% |
| Surgical Line - Suture (Post-op) | 0 (Ideal) | - (Lying not required) | -1 (Trained) | -1 | 0% |
Anesthetic
Surgery is a painful experience, and patients find it difficult to hold still while feeling someone cut into their flesh, which tends to frustrate everyone involved. There are two ways around this: an unconscious (or dead) patient, or powerful painkillers.
Anesthetic (with tank and mask or using the surgery table's integrated anesthesia setup) is a simple and reliable way to render your patient unconscious.
- if the patient's lungs are ruptured, they will occasionally not breath in the anesthetic. Depending on the damage to the lungs, they will either occasionally breath in the anesthetic or it won't work at all. Therefore, you will have to give the patient the anesthetic via Injection, until his lungs are not ruptured anymore.
Operating Table
If you are using an operating table, place your patient on the table (grab your patient, then click the table with your grabbing hand selected). Then buckle them to it to connect the anesthetic system (click hold and drag the patient to the operating table). After a short delay, your patient will be under general anesthetic, which will allow you to operate safely.
- The operating table must have an anesthetic tank attached to be able to put your patient to sleep.
- Click on the surgery table with an anasthetic tank in hand to insert one.
- Click on the table with an empty hand when no patient is buckled to it to remove an existing one.
- If the tank runs out, simply replace it with a new one.
Anesthetic Tank and Medical Mask
If there is no available operating table then you can make the patient wear an anesthetic tank and medical mask and turn on its internals. Encourage your patient to don and activate the tank and mask themselves, as this is much faster than doing it yourself.
- It is advisable to remove the anesthetic tank and medical mask during the cauterizing step for maximum efficiency; the anesthetic takes a few seconds to wear off.
Painkillers
If you don't have anesthetic equipment or you just want to save time, you can give your patients Tramadol or Oxycodone for quick surgeries without anesthetic. These painkillers wear off over time. Tramadol lasts twice as long compared to Oxycodone but Oxycodone has enough painkilling potency to perform Amputations and Alien Embryo Removal. Choose your painkiller wisely.
- Use your medical scanner to monitor your patient's painkiller levels and re-dose as necessary. Using painkillers instead of anesthetics can cause distress in the patient (screaming over the radio about getting operated on without anesthetics, standing up and trying to leave or fight back).
Now that the preparations are done, you can begin with the actual surgery.
Surgeries
Surgeries are simple processes with a series of steps. Once these steps are memorized it should become effortless and routine to perform. Keep in mind that once you have mastery over the basics, it's a good idea to aim to be as fast and efficient as possible due to the importance of recycling casualties back into the fight, or even preventing them from dying in the case of Foreign Object/Alien Embryo Removal.
To perform surgery on someone, you must Toggle the Surgery Mode to be On. This can be bound to a hotkey in preferences. ![]() This will toggle the Help-Intent Safety preference, if you didn't have it already, preventing you from accidentally hurting people with objects when on help intent. You will be forced on to Шаблон:Intent intent (top left, 1)
This will toggle the Help-Intent Safety preference, if you didn't have it already, preventing you from accidentally hurting people with objects when on help intent. You will be forced on to Шаблон:Intent intent (top left, 1) ![]() , which allows you to perform any surgeries.
, which allows you to perform any surgeries.
- The patient must not be wearing any armor.
- Only one surgery can be performed on a given aim-location at a time.
- Once you complete a step in a surgery, you must finish the surgery before you can begin a different one.
- Failing or cancelling the first attempted step doesn't injure the patient unless done deliberately.
- Some steps can be skipped, if the conditions are right, sometimes including the first step.
- If you are in a rush, attempting surgery steps onШаблон:Intent intent (top right, 2)
 deliberately fails the step. For a handful of specific steps, this will quickly and violently complete the step at the expense of your patient's health. Useful when you need to do a critical surgery very quickly, or to save time if you're certain you know what you're doing. It isn't necessary to switch back to Help intent afterwards - that happens automatically. (You can use disarm intent to skip the widening incision with Scalpel or break the rib with Circular Saw)
deliberately fails the step. For a handful of specific steps, this will quickly and violently complete the step at the expense of your patient's health. Useful when you need to do a critical surgery very quickly, or to save time if you're certain you know what you're doing. It isn't necessary to switch back to Help intent afterwards - that happens automatically. (You can use disarm intent to skip the widening incision with Scalpel or break the rib with Circular Saw)
Standing Patients and Self-Surgery
Some surgeries can be performed on a patient who's standing up. These surgeries aren't affected by the surface under the patient. These are marked as (STANDING).
Some surgeries can be performed on yourself. As you need to be able to hold tools while you work, this means they have to be able to be performed on a standing patient, since people who're lying down can't handle objects. These are marked as (SELF).
- If you're trying to work on a standing patient and can't begin a surgery that you know you should be able to, make sure that it doesn't need them to be lying down.
- Since it's difficult and awkward to work on your own body, self-surgery takes longer to do.
- You can't perform surgery on the same arm you're holding the tool with.
- Self-surgery requires you to use painkillers rather than anesthesia, since it's hard to work when unconscious.
Required Skills
Your character's training affects how quickly they can work and mitigates risk of failure due to improvised tool or unsuitable working condition penalties.
Some surgeries can be performed by anyone with any surgical training, but others need a more thorough education.
Medics, nurses, and pilot officers all have basic surgical training and can perform simple level 1 surgeries.
Doctors, chief medical officers, and synthetic units have more skills and can perform level 1 and level 2 surgeries.
You may occasionally see Professor DUMMY, the medical mannequin. This is a sophisticated training tool designed to realistically simulate any wound (Except alien parasite infections). Real patients are more difficult to perform surgery on - a medic may be able to set Professor DUMMY's broken ribs, but that doesn't mean they can do it on a real patient in the field. (You may contact your local CMO to vend the Professor DUMMY from their cabinet)
Level 1 Surgeries
(Cautery) (optional)
| Surgery: | Description: |
|---|---|
| Suture Wound (Everywhere except mouth/eyes.) (STANDING - SELF) | Suture and tend a wound that has brute or burn damage on it. This will heal 10 brute on the targeted area when a surgical line is used, and will heal 10 burn if a synth graft is used. This will loop until half of all damage on the area has been fixed.
|
| Foreign Object (Everywhere except mouth/eyes.) | Removal of unknown objects, such as shrapnel or implants from the body.
|
| Sealing a Stump (Severed Arms and Legs) | Sealing a stump where the patient's arm or leg should have been.
|
| Autopsy (Only on Permanently Dead) | Helps find out how the person died. Displays wounds, possible causes, and detected chemicals in the body.
|
| Internal Bleeding Surgery (Everywhere except mouth/eyes.) | This surgery mends the torn/ripped arteries and veins within the body to stop internal bleeding.
|
Level 2 Surgeries
| Surgery: | Description: |
|---|---|
| Alien Embryo Removal | Removal of an alien embryo from the body.
|
| Bone Repair Surgery (Everywhere except mouth/eyes.) | This surgery is used for mending broken bones and fractures.
|
| Internal Organs Surgery (Groin, Chest.) | Mending broken internal organs such as the heart or appendix. Note that this surgery excludes the eyes and brain as they have their own surgeries respectively.
|
| Monkey Cube Removal (Chest.) | Removing a monkey cube post-ingestion. This surgery is one of the few that require a surgical drill.
|
| Eye Surgery (Eyes.) | Mending the eyes to cure blindness and eye damage. |
| Brain Damage Surgery (Head.) | Fixing up the brain.
|
| Facial Reconstruction Surgery (Mouth.) | This surgery fixes facial deformities caused by severe damage to the head. I.E. "Unknown as (name)" when speaking. |
| Amputation (Limbs: Legs, Arms, Hands, Feet.) | This surgery removes a limb. This surgery is usually pointless to do.
|
| Limb Replacement Surgery (Limbs: Legs, Arms, Hands, Feet.) | The replacement of missing limbs with robotic ones. Robot arms and legs are used to replace hands and feet; there is no need to further amputate if that's all the patient has lost.
|
| Synthetic Head Re-Attachment Surgery (Head.) | Re-attaching a decapitated synthetic head.
Note: There isn't a timer on defibbing a synthetic.
|
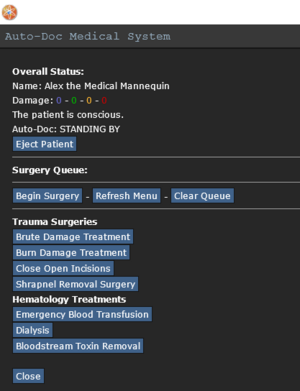
The Autodoc System
The Autodoc system is located in the middle of the treatment center and is only usable by medical staff (and Squad Medics during Whiskey Outpost). Note that while the Autodoc is a useful machine in medical, it is limited in what surgeries it is able to perform, requiring upgrades from Research for procedures such as Bone Fracture Surgery, or Alien Embryo Removal.
| Manual: | Manual mode will perform all selected surgery types once "Begin Surgery" is selected, and the procedures are done in the order they are selected, and will repeat itself if necessary (ex. multiple incisions are open)
Combining SurgeriesOften people will come in with multiple problems at once. For instance, you might have a patient who has a fractured skull, brain damage, and shrapnel in their head. Performing three separate surgeries is time consuming when other marines may be waiting. The following procedures are examples of combining multiple procedures at once. It is possible to condense the previous surgery down to one in such a manner:
Well what about an infected marine with a broken chest, internal bleeding, and a ruptured lung? Here you will need to use medication from the vendors in Medbay in order to tackle the problems at hand.
Tips
|